Chances are you’re familiar with the terms LTE and 5G, but do you truly grasp their meaning and differences? This comprehensive comparison between LTE and 5G aims to shed light on these distinct cellular standards, enabling you to grasp their divergences and grasp the potential benefits that 5G might offer.
What are LTE and 5G exactly?
LTE and 5G are wireless communication standards. LTE, short for Long Term Evolution, is an upgraded version of 4G, which stands for fourth-generation wireless. Many LTE networks actually use a further iteration called LTE-A (Advanced), though it’s commonly referred to as LTE.
5G is the next step in wireless technology, representing the fifth generation. Generally, higher generations offer better speeds and performance. Instead of delving into the specific improvements brought by 5G, let’s first focus on the technical differences in network hardware.
All wireless networks rely on cell sites to transmit data through radio waves, but the methods can vary significantly. 4G carriers use high-power cell towers capable of broadcasting signals over long distances. They utilize different frequencies, such as 800, 1800, and 2600 MHz bands, and some carriers also employ 700, 1900, and 2300 MHz bands. For a more detailed explanation of LTE workings, you can refer to our 4G LTE guide.
5G technology combines a blend of established and innovative technologies to deliver the fastest and most responsive coverage available. Its primary objective is to unlock additional wireless spectrum, which translates into increased capacity and faster overall speeds. This is achieved by introducing new high-frequency bands and repurposing unused frequencies from sources like radio and TV. Two pivotal categories within the realm of 5G are mmWave and sub-6GHz.
The mmWave technology operates on high-frequency bands and provides unparalleled speeds. However, its coverage range is relatively short. The advantage lies in the compact size of the mmWave base stations, which can be easily mounted on buildings, lamp posts, and other structures. Carriers like Verizon deploy these smaller towers extensively in select U.S. cities, allowing major metropolitan areas to enjoy the fastest 5G speeds.
On the other hand, sub-6GHz networks employ signals similar to Wi-Fi, operating slightly above the conventional 4G LTE frequencies. This range, spanning from 3 to 6GHz, offers a flexible and long-distance reach, serving as the foundation for most 5G networks. Although these cell stations are larger than mmWave stations, they are still smaller than traditional LTE cell stations. If you reside in a small city or rural area with access to 5G speeds, it is likely based on the sub-6GHz standard.
Which One is Faster Among LTE & 5G?
The actual speeds provided by LTE and 5G networks vary depending on the carrier. However, in most cases, 5G outperforms LTE in terms of speed. Equally important is latency, as lower latency ensures faster data transfer and a smoother mobile experience. This translates to shorter load times for streaming content, reduced lag in gaming, and an overall enhanced internet experience.
While modern LTE-A offers impressive speeds, reaching up to 100Mbps or more, the actual average speeds tend to be lower, ranging from 15-60Mbps for most users. Latency typically falls within the 25-50ms range and can vary based on location.
Although LTE speeds are more than sufficient for most downloading and gaming needs, 5G holds the promise of even better performance. Theoretically, 5G can reach top speeds of 10Gbps with extremely low latency of around 1mm. While real-world performance may not match lab conditions, most current 5G networks in the United States offer average speeds of at least 75Mbps with a latency of 20ms or less, often exceeding these benchmarks.
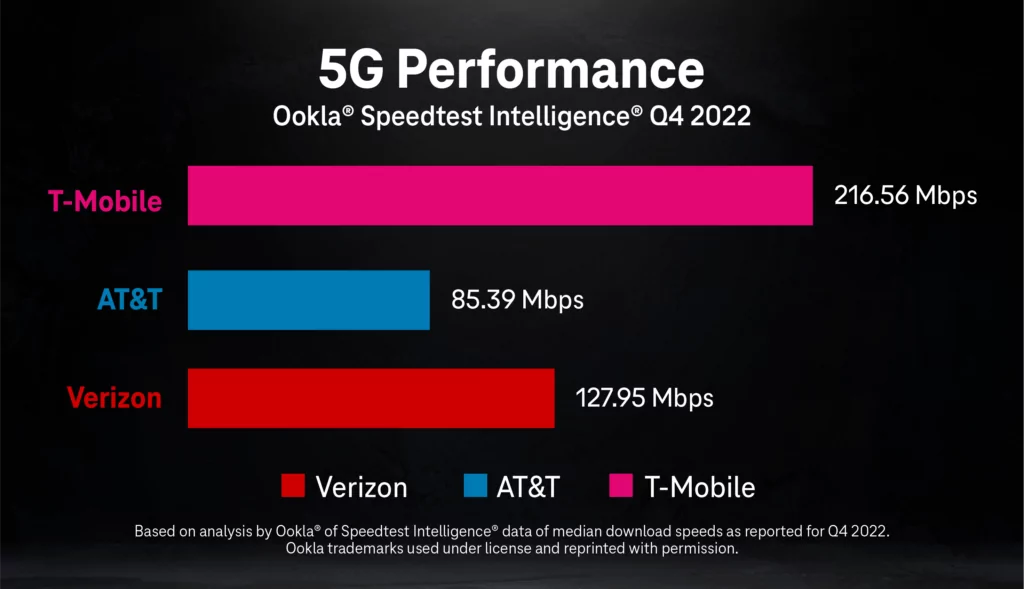
According to a recent report by Ookla, T-Mobile emerges as the fastest 5G network in the US, boasting an average speed of 216.56Mbps. Verizon and AT&T follow with average speeds of 129.96Mbps and 85.39Mbps, respectively.
Advantages of 5G Apart From Faster Speeds
5G, with its super-fast speeds and minimal latency, plays a crucial role in transforming various industries, such as connected cars, smart city technology, virtual reality, mixed reality, autonomous vehicles, and industrial automation. Additionally, 5G is making waves in the realm of home internet, offering competition to traditional cable connections with its impressive speeds.
However, when it comes to smartphones, the leap from 4G to 5G may not be as revolutionary as the transition from 3G to 4G. While 5G is set to become increasingly faster in the future, surpassing the capabilities of LTE-A, we haven’t reached that stage just yet. Nevertheless, 5G offers several advantages that directly benefit smartphone users.
One significant advantage is the expanded bandwidth, leading to seamless data transfers and more reliable performance. This translates to fewer instances of quality drops and related issues when engaging in high-bandwidth activities like streaming on LTE.
Another notable feature of 5G is network slicing, which sets it apart from LTE. This capability enables different parts of the network to specialize in specific tasks. For instance, a dedicated portion of the network can focus on gaming, while another segment prioritizes high-definition streaming. Ultimately, this optimized traffic management reduces congestion and enhances overall network performance.
The true power of 5G lies in its future potential rather than its current capabilities. While it already offers significant speed and serves as a valuable upgrade over LTE, its importance will become more pronounced in the coming years as our demand for bandwidth grows. The International Telecommunications Union has set ambitious benchmarks for 5G compared to LTE, envisioning:
- 10 times increase in battery life for low-power communications
- 5 times reduction in latency (end-to-end)
- 100 times increase in the number of connected devices
- 100 times improvement in user data rates
- 1000 times increase in mobile data volume per area
LTE isn’t Going Away Anytime Soon
The good news is that you don’t have to choose between LTE and 5G. These technologies are designed to work together, ensuring optimal coverage regardless of your location.
LTE is here to stay for the foreseeable future, following the pattern of 3G and 4G coexisting for a long time before the latter was phased out. Similar to this, it is expected that LTE will remain in use for at least another decade before being replaced by 5G.
Implementing new networks is a time-consuming process. Additionally, 5G currently has limitations in terms of long-distance coverage, which means LTE will continue to be important until advancements in 5G technology bridge this gap. Even if you have a 5G phone, LTE serves as a fallback option in areas where 5G is not yet available.
It’s worth noting that LTE technology is significantly cheaper than 5G, both in terms of device antennas and tower equipment. While more mid-range devices are incorporating 5G, budget devices will likely continue to rely on LTE until 5G becomes more mature.
For more such tips, updates and learning resources, stay tuned to Insitebuild Blog.






